|
Accessing prior knowledge is an important element of instruction especially when serving multilingual learners. It doesn’t have to take long, but when implemented it can stimulate thinking and help new learning stick too.
ABC Brainstorming is one way to access prior knowledge, and it can also be used as a culminating activity. ABC Brainstorming can be done in small collaborative groups or it can be done individually. I have found it most effective when introduced first individually for a few minutes and then in small collaborative groups. Multilingual learners (MLs) are amongst the fastest growing population in the United States. MLs come from diverse linguistic and cultural backgrounds. The assets they bring to classrooms are sometimes underrecognized leaving these students struggling linguistically and academically. Many teachers of MLs want to provide instruction that meets their needs but find themselves not knowing how to help and feeling overwhelmed.
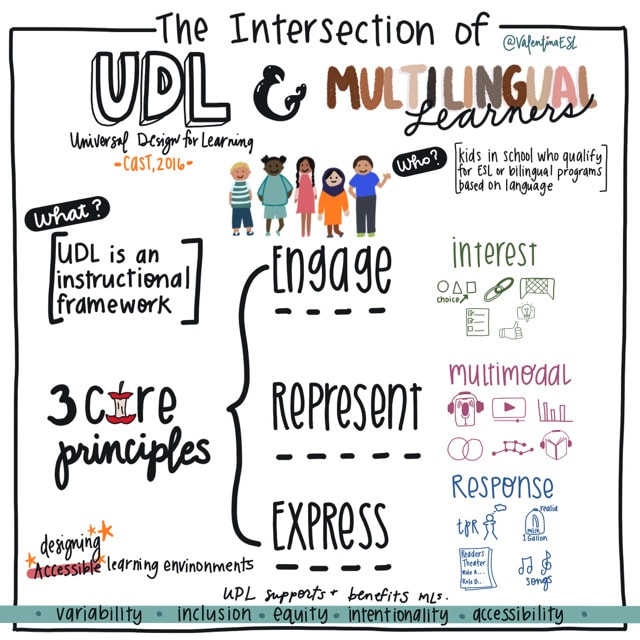
This is where Universal Design for Learning (UDL) enters and has been known to support and benefit MLs. What is UDL? Last year this article was shared and greatly loved. This year, I'm adding to it to include one additional support.
Multilingual learners count on us to provide high-quality, comprehensible, and culturally responsive instruction in each lesson in every classroom. Here are 23 practical and efficient ways (in no particular order) we can support multilingual learners as they climb to become our future global leaders. *The terms multilingual, emergent bilingual, and English learner are used interchangeably in this article and also include the acronyms MLs, EBs, and ELs. I have fond memories of cuddling up next to my tata (Serbian for daddy) before bedtime and listening anxiously as he told stories he remembered or even ones he made up. As an immigrant family from the former Yugoslavia, we brought little with us when we came to America. Books were heavy and did not make the journey. Storytelling, however, was a cherished time in our home. My favorite story was Hansel and Gretel.
**a version of this blog post was first published on BookBuzz.
This brief post lists 13 instructional practices that reduce the love and motivation for reading in students and then 13 ways to inspire and motivate them.
In contrast, here are 13 ways to help students find love, joy, and excitement in reading. Multilingual learners count on us to provide high-quality, comprehensible, and culturally responsive instruction in each lesson in every classroom.
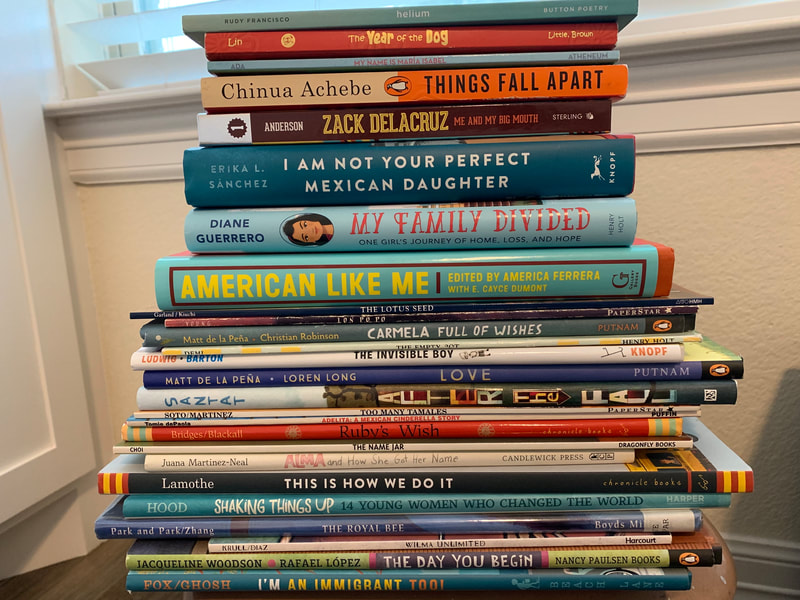
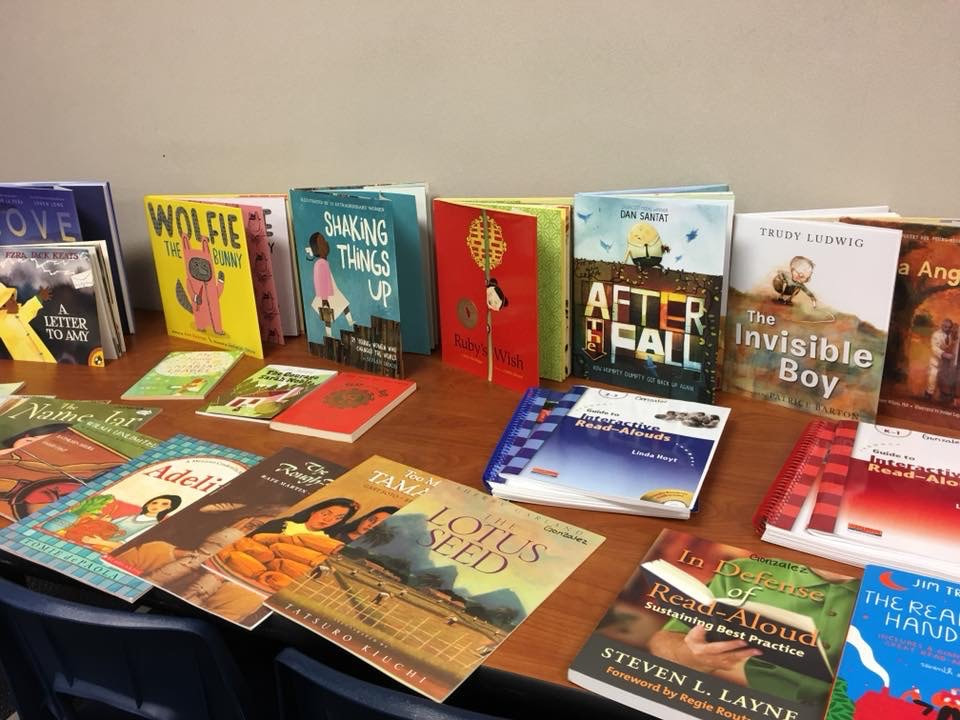
Here are 22 practical and efficient ways (in no particular order) we can support emergent bilinguals as they climb to become our future global leaders. *The terms multilingual, emergent bilingual, and English learner are used interchangeably in this article and also include the acronyms MLs, EBs, and ELs. This article was first published on 6/8/2018 and updated on 8/21/2021. When I first saw the graphics below that showed the diversity represented in children's books, I was stunned and appalled. You can learn more about the article here. The statistics were alarming. They reported that the majority of main characters depicted in children's books are either White or Animals/Objects. Seeing these graphics and reading about the study led me to take an audit of my own books and resources. I started by sorting out my books. I made stacks. And honestly, I was shocked and saddened that my bookshelf truly was not as diverse as I imagined. It certainly did not parallel the demographics on my campus either. This prompted action. Students benefit from seeing themselves and others in the books they read. Why? For one, because seeing ourselves outside of ourselves makes us feel visible. In this video, Rene Watson, an author and educator, shares how important it is for students to read about about characters that are like them and share similar experiences. Rudine Sims-Bishop calls these books mirrors. On the other hand, readers also need to read about a wide variety of people and experiences. Sims-Bishop calls these windows. Reading about other's lives helps us to find connections and build community. Dr. Brene Brown says, "We are hardwired for connection and without it there is suffering." We also gain much knowledge and learn empathy from seeing others in the books we read. So why aren't our shelves filled with books that have diverse characters? If you've ever questioned why your students aren't interested in the books on your shelves, you might stop to think about the types of books that are there. Do they represent your students? Can the kids connect with them? I also learned about a non-profit organization called We Need Diverse Books. Check it out. They share a lot of information including lists of diverse books. In my quest for making my shelf more diverse, I have found some great books. I'll keep adding to this and if you have suggestions, please comment and include a picture if you can. If you like what you read and would like to read more like this, you may enjoy the book Reading & Writing with English Learners: A Framework for K-5 by Valentina Gonzalez and Dr. Melinda Miller.
Teaching multilingual children is a gift. It’s truly a joy. In my own classroom, I learned so much from my students, especially those that spoke more than one language.
Over the years, one thing I learned from experience as well as through professional learning is that each student deserves to be seen and served individually. No one size fits all approach works. While differentiation may seem daunting, it’s actually not that scary. Dr. Stephen Fleenor describes differentiation as “not creating individualized lessons...it is creating environments in which students at all different levels, all different proficiencies...can each thrive and each grow one level up in that lesson”. Dr. Fleenor offers two wise suggestions for creating of environments that offer differentiation: This article was originally shared on the Seidlitz Blog on April 29, 2020.
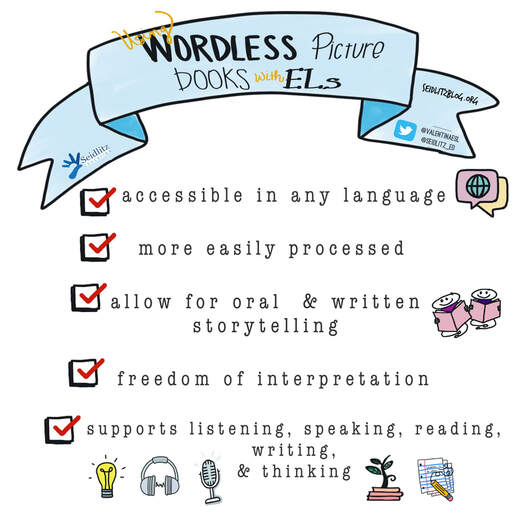
Imagine you are a second grade student born in America, and you only speak English. You’ve attended English schools until now. But your father’s job has relocated your family to France, and now you are in a classroom filled with students and a teacher who only speak French (a language you have never spoken). The science teacher hands you a book and signals for you to read it. You open the book and find that it is filled with pictures…no words. First a group of horses. A mare feeding a foal. A colt running wild. Then a group of pigs, chickens, cows, etc. Instantly, you begin to think about the information you know about animals. What they are called, where they live, what they eat, etc. Though you aren’t able to communicate this information in French yet, you are able to follow along with the class and think in English using the schema and background knowledge you have about animals. Why Use Wordless Picture Books? Art teacher, Libby Beaty, teaches in Seoul, South Korea at Seoul Foreign Middle School. I came across her Twitter handle in April and was instantly hooked. But I didn’t know how much I would actually love her until after I asked her to answer a few questions for me. When I read her responses, my heart filled with joy and I couldn’t wipe the smile off my face. It was Teacher Appreciation Week and this is yet another example of a teacher we must celebrate!
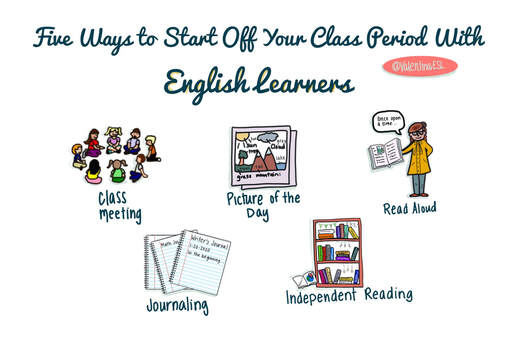
Here's the art project that Libby shared on Twitter and that she had her students do. It went pretty much viral. When I saw it, I reached out to Libby on Instagram and asked if I could “interview” her about her work. I asked her a series of questions. Here’s how it went. The first thing we do with students can set the tone for our time together. Starting the period off on the right foot is critical to a successful lesson. Read on to discover five ways to start your class period in engaging and welcoming ways whether you are a general education teacher or an ESL teacher that pulls students out.
This November 2017, I had the honor of being a featured speaker at our state conference, TexTESOL 2017. The event was a huge success- overall due to the hard work that the TESOL IV board put into organizing such a massive conference. The keynote speakers included THE Stephen Krashen and John Seidlitz, both heroes for me in the ELL world. If you've read any of my other posts, you know that I read and recommend several of John's books. And who in the ESL world doesn't love Krashen?
Let's back up a little and break it down. What is culture? Culture has many meanings and it depends on who you ask or which source you use. If you review most definitions, they all have somethings in common. Zion and Kozleski describe culture as the "shared beliefs, views, values, customs, behaviors and artifacts that the members of society use to interact with their world and with one another (as cited in Fenner & Snyder, 2017).
From this definition, I know we can gather that everyone has a culture. We all have beliefs and views. We all carry values and customs. We all have certain behaviors and artifacts related to our own society that we use to interact with the world and with others. This leads me to the conclusion that being culturally responsive is not only going to benefit my English Learners, it will benefit every child in my classroom. |
Categories
All
|












































 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
