|
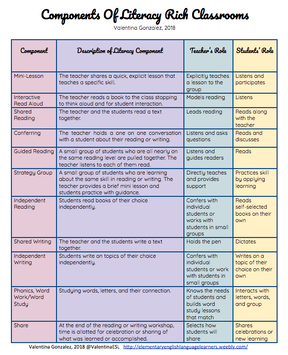
In the last post the focus was an overview of literacy components. This article will zoom in on just the mini lesson. The goals are to:
0 Comments
The next few posts will be related to one another regarding the topic of literacy instruction as it pertains to English learners. The focus will be specifically on supporting English learners in English Language Arts classrooms and accommodating instruction and materials to promote growth and success.
But let's begin by setting the foundation for our work with some common definitions or terms.
A huge part of balanced literacy and a workshop setting is conferring with students. Conferring allows for maximum differentiation to meet specific instructional needs for students. But when we serve students who are also learning English, there is a need to accommodate the way we confer. After years of conferring with ELLs and tons of reading in the field, here are my tips for conferring with ELLs.
This is a post I wrote for Tan's Blog. It was shared on EmpoweringELLs in May 2017.
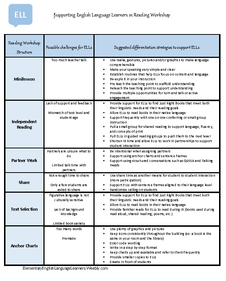
When I stop to reflect on what is BEST practice for my elementary ELLs in reading, writing, listening, and speaking, the answer comes to me quite clearly…the workshop model. Why? What I know about the needs of my ELLs is that they require explicit instruction, modeling, guidance, routine, and practice. Here’s how the reading and writing workshop models promote progress for ELLs in listening, speaking, reading and writing. The longer I have been in education, the stronger I believe in small group instruction. It truly is the heart of instruction. In a small group, the ratio between student and teacher is drastically reduced allowing the teacher to identify individual student needs and easily differentiate instruction.
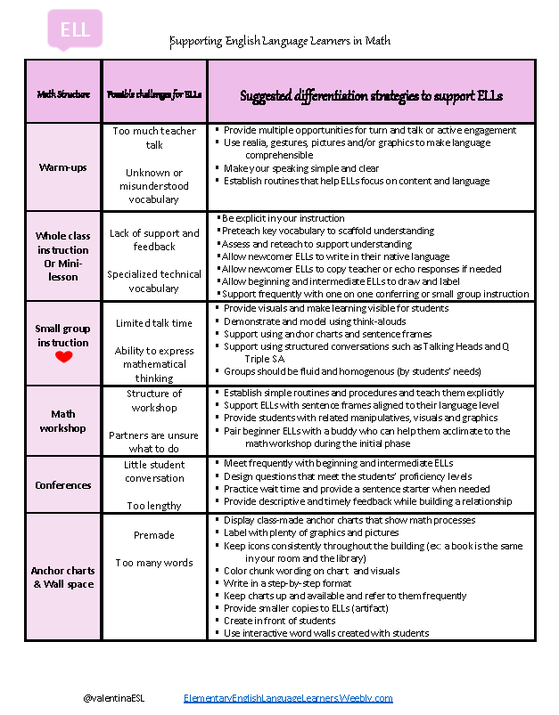
No matter the content area in elementary school, small group instruction has a greater effect on student learning than whole group. Some may say that it's too difficult to pull small groups so they continue to instruct in a whole class setting. I agree that in the beginning it may be difficult to get the structure and routine down for both the teacher and the students; however, once good classroom management is put into place and the routines are set, the ball will get rolling and small group becomes the best way to teach. After all, as educators I think there aren't many who don't agree that we want to do what is best for students. While whole group instruction may be easiest for teachers to plan and implement, it can't be best for students who are diverse and unique--all at various levels with different background knowledge. Overall, most teachers are pretty good at pulling small groups for reading instruction in the primary grades. But even that seems to taper off around third grade. What we know is that when we gather a small group of roughly 4-6 students and give them what they specifically need at the moment greater progress occurs in language and in content knowledge. So why don't we continue to pull small groups as kids get older? And how about pulling them in other content areas such as math, science, and social studies? Some may wonder...What are the other kids doing while I pull a group? Won't they get off task? Well, that's up to you as the teacher. The Benefits of Small Groups: For ELLs one of the other benefits of small group instruction is that it lowers the affective filter. You know that feeling of fear or anxiety when you are in a situation that is high stress? Well, English Language Learners can feel that anxiety in a whole group setting more than in a smaller setting. When everyone is waiting and all eyes are on you anticipating your response it can be intimidating. This feeling is amplified when you are new to the country, have an accent or need a great deal of support. When teachers meet with students in small groups, they are more apt to individualizing instruction and truly meeting students where they are. In a smaller setting, teachers are able to ask more questions to individual students which allows the students to interact more with the teacher. This also has an added benefit which is building the student teacher relationship. Another benefit of small groups is that students are given more opportunities to talk. When students are in a smaller setting, they feel freer to talk, ask questions and grapple with ideas. This allows them to think critically and negotiate for meaning while having academic discussions more openly. On the other hand, in a whole group setting, the teacher asks a question and one student responds while everyone else zones out.  I must confess. I'm not a math specialist. In fact, as a classroom teacher, I've never taught math myself. I have supported math as an ESL Specialist in a co-teach position but never taught my own math class. However, what I can offer are linguistic supports for teaching in a math setting. The misconception out there is that math is a universal language. This is far from true. Math is supported by language and if students are learning English, then learning math in their target language can be a struggle. If you take anything away from this document, I hope it's that your ELLs NEED to talk about math using key vocabulary and may need sentence stems as scaffolds for conversation. Talk, or academic conversation, helps students develop language while internalizing learning, negotiating for meaning and cementing learning. Please feel free to share this document with others as I hope it benefits language learners. If you have other suggestions or comments regarding math and ELLs, they are welcome here. Resources I leaned upon: Bresser, R., Melanese, K., & Sphar, C. (2009). Supporting English language learners in math class: grades 3-5. Sausalito, CA: Math Solutions Publications. Bresser, R., Sphar, C., & Melanese, K. (n.d.). Supporting English Language Learners in Math Class, Grades K-2. Driscoll, M., Nikula, J., & DePiper, J. N. (2016). Mathematical thinking and communication: access for English learners. Portsmouth, NH: Heinemann.
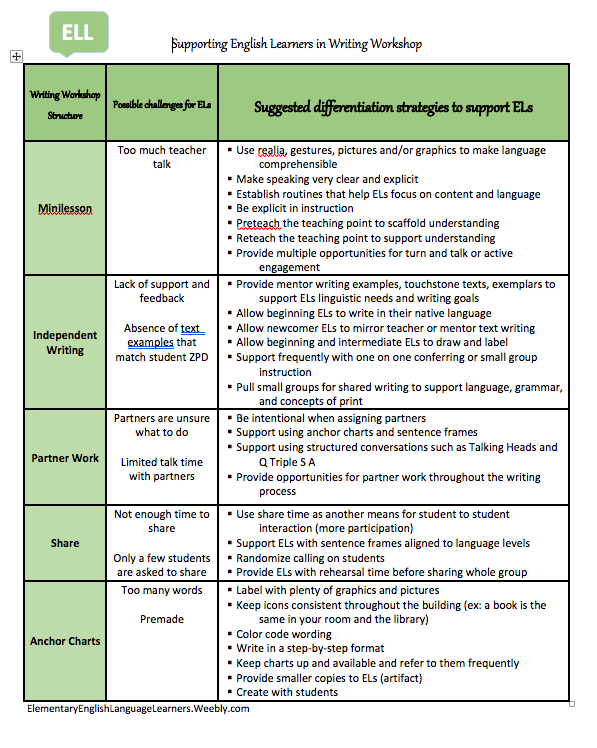
English Language Learners benefit greatly from the structure of Writing Workshop. However, there are a some small tweaks we can make as teachers to scaffold instruction for ELLs and truly make the experience advance both literacy and language. ELLs vary vastly. Some are born in the United States and experience similar American cultures and traditions. Others have little formal education or come to America with drastically different cultures and traditions. Factors such as age, intrinsic motivation, proficiency in native language, and educational background also affect the student's development of English. For these reasons and more, we have to take a good look at each child individually and know how to adjust the Writing Workshop so that the child will grow as a writer because of the workshop structure. What I noticed in classrooms is that teachers are embracing the Writing Workshop. But some feel they can't vary from the pages of Units of Study or other programs they use. This isn't true. We have to remember, we are teaching students first. If we keep students at the forefront we can't go wrong. With sequenced, targeted, and focused support in writing, ELLs can make leaps and bounds! Here is how I support English Language Learners in Writing Workshop. Download is available below the picture.
|
Categories
All
|
||||||||||||






 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
