|
This is a monolingual brain. This is a brain on multiple languages. In a globalized society, it is a disadvantage to understand and speak a single language. Nations work together to solve problems as well as communicate and work alongside one another. Therefore, one who is able to speak and understand multiple languages has apparent advantages in communication over one who can not.
Let’s examine the brain, languages, and how this plays out in our classrooms. The F-Word. Fidelity & Why it May Be a Fallacy for EL InstructionBuzzwords in education are like mosquitos. They are here for a while and during that time they become very annoying. Lately, many educators are hearing one certain F word frequently in regard to programs and curriculum.
FIDELITY Multilingual learners (MLs) are amongst the fastest growing population in the United States. MLs come from diverse linguistic and cultural backgrounds. The assets they bring to classrooms are sometimes underrecognized leaving these students struggling linguistically and academically. Many teachers of MLs want to provide instruction that meets their needs but find themselves not knowing how to help and feeling overwhelmed.
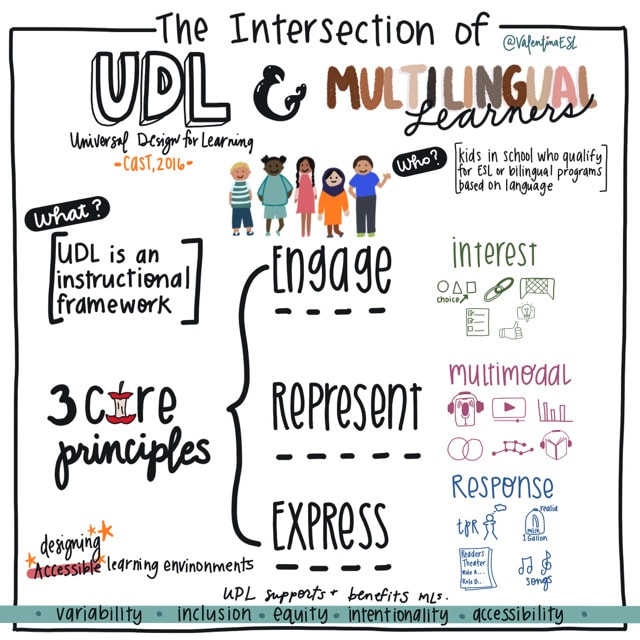
This is where Universal Design for Learning (UDL) enters and has been known to support and benefit MLs. What is UDL? Last year this article was shared and greatly loved. This year, I'm adding to it to include one additional support.
Multilingual learners count on us to provide high-quality, comprehensible, and culturally responsive instruction in each lesson in every classroom. Here are 23 practical and efficient ways (in no particular order) we can support multilingual learners as they climb to become our future global leaders. *The terms multilingual, emergent bilingual, and English learner are used interchangeably in this article and also include the acronyms MLs, EBs, and ELs. Multilingual learners count on us to provide high-quality, comprehensible, and culturally responsive instruction in each lesson in every classroom.
Here are 22 practical and efficient ways (in no particular order) we can support emergent bilinguals as they climb to become our future global leaders. *The terms multilingual, emergent bilingual, and English learner are used interchangeably in this article and also include the acronyms MLs, EBs, and ELs. Teaching multilingual children is a gift. It’s truly a joy. In my own classroom, I learned so much from my students, especially those that spoke more than one language.
Over the years, one thing I learned from experience as well as through professional learning is that each student deserves to be seen and served individually. No one size fits all approach works. While differentiation may seem daunting, it’s actually not that scary. Dr. Stephen Fleenor describes differentiation as “not creating individualized lessons...it is creating environments in which students at all different levels, all different proficiencies...can each thrive and each grow one level up in that lesson”. Dr. Fleenor offers two wise suggestions for creating of environments that offer differentiation: Often I'm inspired to write by something I've encountered either through reading a professional book, visiting a campus or classroom, or through conversation (in person or online). This post was inspired by recent conversation online. Let me set it up for you.
A teacher wanted advice regarding a student she has who is new to the United States. The student's primary language is Spanish and the teacher is having difficulty serving the student in a main stream English classroom while also serving the other English only students. The teacher mentioned that she had yet to have a conversation with the student. Many other teachers responded giving advice. Some said it's impossible to help this child. Others said that the student first must learn English before she can learn grade level content. Some said the other students in the class will suffer if the teacher employs techniques to support the one beginner. This post was completely deficit based and many of the comments to it really touched a nerve. "I see no benefit in having her..." So if you feel that you're in a similar situation or you know someone who is, here's some advice: How to handle resistance from teachersThis topic has been rolling around in my mind for quite some time. I hear about the problem from EL teachers around the nation. Not to mention that as an EL teacher myself, I encountered this struggle too many times.
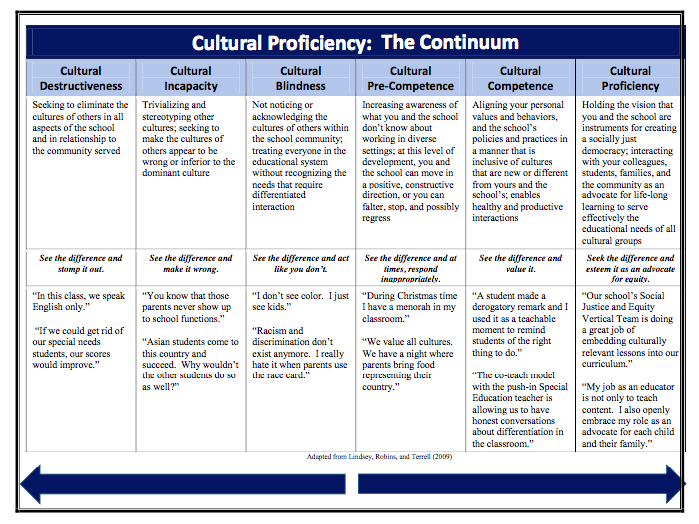
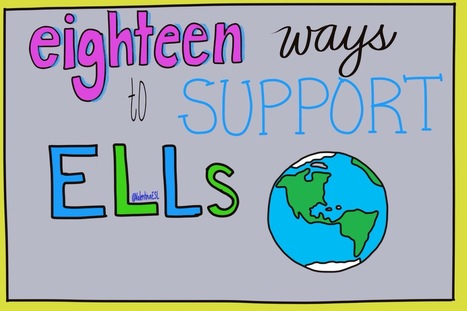
I remember vividly having a meeting with a gen ed teacher. One of our students was struggling in her class. He hadn't been in the US very long, only a bit over a year. So I asked that we meet to discuss how I could help to plan with her and accommodate instruction. I was met with resistance from the moment I walked in the room. The teacher explained that she felt that this student (along with all the other ELs) should not have anything different than everyone in the class. She explained that she has heard him speak and that he is capable of doing the work. She went on to tell me that the grades were reflective of defiance and not ability. Ouch. I listened. Quietly. But it was difficult. And then when she finished, I carefully shared with her his language levels in each domain explaining the difference between social and academic language. We took a look at the types of accommodations that were appropriate for a learner at his language proficiency. In the end, it took a while for this teacher to come around. It took support, scaffolding, and leading the teacher to find the best way to make progress with the student. And to begin with, rebuilding their relationship came first. This student needed to know that the teacher genuinely cared about his education and growth. So what can you do if you are faced with a similar dilemma? Here are a few tips I've learned along the way: 1. Build a caring relationship with the teacher. The teacher will not trust you unless a solid foundation is there. Begin with casual conversations that have nothing to do with school. Get to know the teacher beyond work. Ask personal questions (but not too personal). Then start talking about content. Discuss the learning that's happening in the classroom. Finally talk about specific students, how they are doing, what they need to succeed, etc. This will not happen in one day, not in a week...it will take time. 2. Scaffold the teacher's learning. Model for the teacher (if you can) what you would like for him/her to do with students. If the teacher would benefit from understanding language development, scaffold that instruction for them. Introduce it in small chunks or provide visuals. 3. Model lessons. The best professional development is learning from other educators or our peers. Model lessons for the teacher that highlight accommodations. If you are a co-teacher, then this will work out great. If this is not possible, set up a time when the teacher can observe another educator to see a lesson. This is great because it not only helps your teacher who is struggling but also builds capacity for the other teacher. 4. Suggest professional learning opportunities. When the teacher is open to learning more, suggest professional development that will help to build on their practice. In-district PD, out of district PD, online learning, professional books, or twitter chats, are excellent. Each teacher will have their own learning style. Some like face to face while others prefer to read on their own or learn on line. The good news is that there are many options available these days. Being culturally aware and responsive to our students' needs is critical to their success. The more we support them during their learning, the better they will perform when it counts. I have found it helpful to share this cultural proficiency continuum (shared with me at a training) with educators and let them self-reflect. 18 ways to Support English Learners in your classroom in 2018 (or EVER!)2018 is going to be a year where your English Learners thrive! Your ELs need some extra scaffolds and supports to level the playing field. They are learning a new language while navigating content at the same time.
Here are 18 ways that you can help support them with their journey. Not every EL will need all of these scaffolds. Some will need more than others. And once they no longer need the scaffold, remember to release it and let them soar! Create a Welcoming Environment
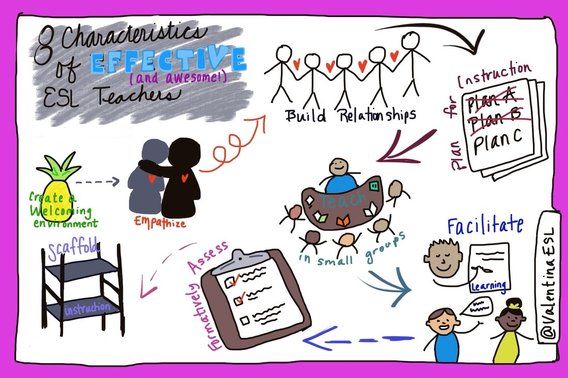
1. The BEST ESL teachers know how to make their students feel safe and valued. They are able to break down the walls of anxiety and fear so students feel ready and eager to learn. These teachers do this by using verbal and nonverbal cues. The way they speak with their students tells them that they are wanted, valued, and loved. These teachers make room for all students.
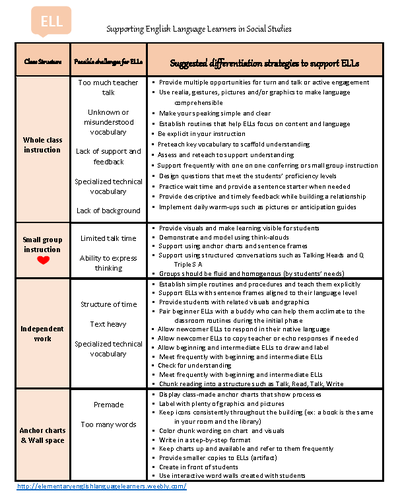
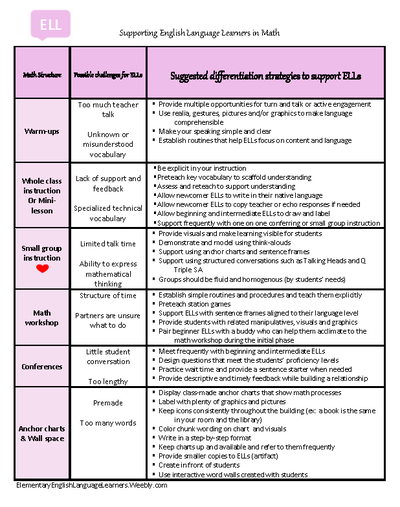
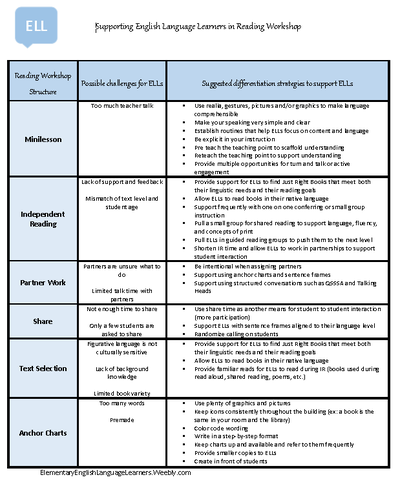
These supporting documents have been in high demand and are in various blog posts on this blog. So I decided to put them all in one post for easy access. This is a one stop shop where you can find the supporting documents to shelter instruction in the content areas. Please feel free to share them with your teacher colleagues as they are meant to help all educators and students. These supports are not just for English Language Learners. ALL learners who need extra help will benefit!
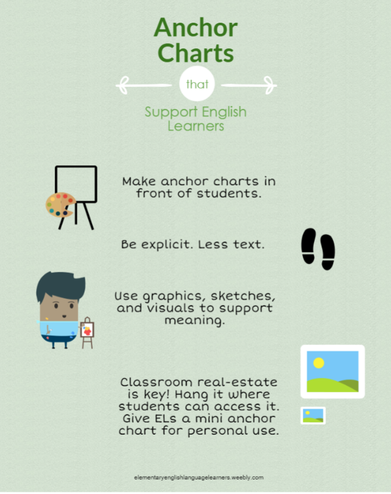
Have you ever walked into a classroom and looked around in awe at the beautiful charts and posters? The beautifully decorated boarders and store bought matched sets? But when you ask the students about them, they don't have a clue what they are for or how to use them?
|
Categories
All
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||









 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
