|
Multilingual learners count on us to provide high-quality, comprehensible, and culturally responsive instruction in each lesson in every classroom.
Here are 22 practical and efficient ways (in no particular order) we can support emergent bilinguals as they climb to become our future global leaders. *The terms multilingual, emergent bilingual, and English learner are used interchangeably in this article and also include the acronyms MLs, EBs, and ELs.
1 Comment
This article was originally shared on the Seidlitz Blog on April 29, 2020.
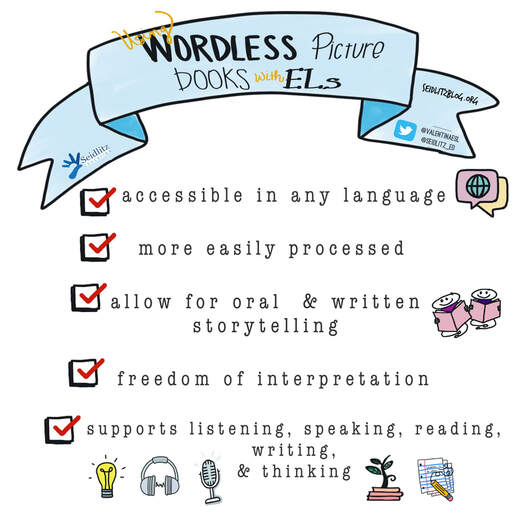
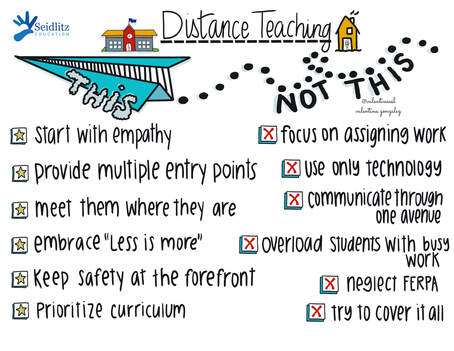
Imagine you are a second grade student born in America, and you only speak English. You’ve attended English schools until now. But your father’s job has relocated your family to France, and now you are in a classroom filled with students and a teacher who only speak French (a language you have never spoken). The science teacher hands you a book and signals for you to read it. You open the book and find that it is filled with pictures…no words. First a group of horses. A mare feeding a foal. A colt running wild. Then a group of pigs, chickens, cows, etc. Instantly, you begin to think about the information you know about animals. What they are called, where they live, what they eat, etc. Though you aren’t able to communicate this information in French yet, you are able to follow along with the class and think in English using the schema and background knowledge you have about animals. Why Use Wordless Picture Books? If you'd like to watch the free, brief webinars that Tan Huynh and I did on Reading and Writing with ELs during Distance Learning, they are available on this website along with the presentation slides. Stay well friends. Pivoting instruction to meet the needs of students and families has been a challenge for teachers across the world since the COVID-19 pandemic. But through collaboration and continued support, we are working together to serve students. Thank you all for everything you are doing to ensure that ELs are receiving the support they need.
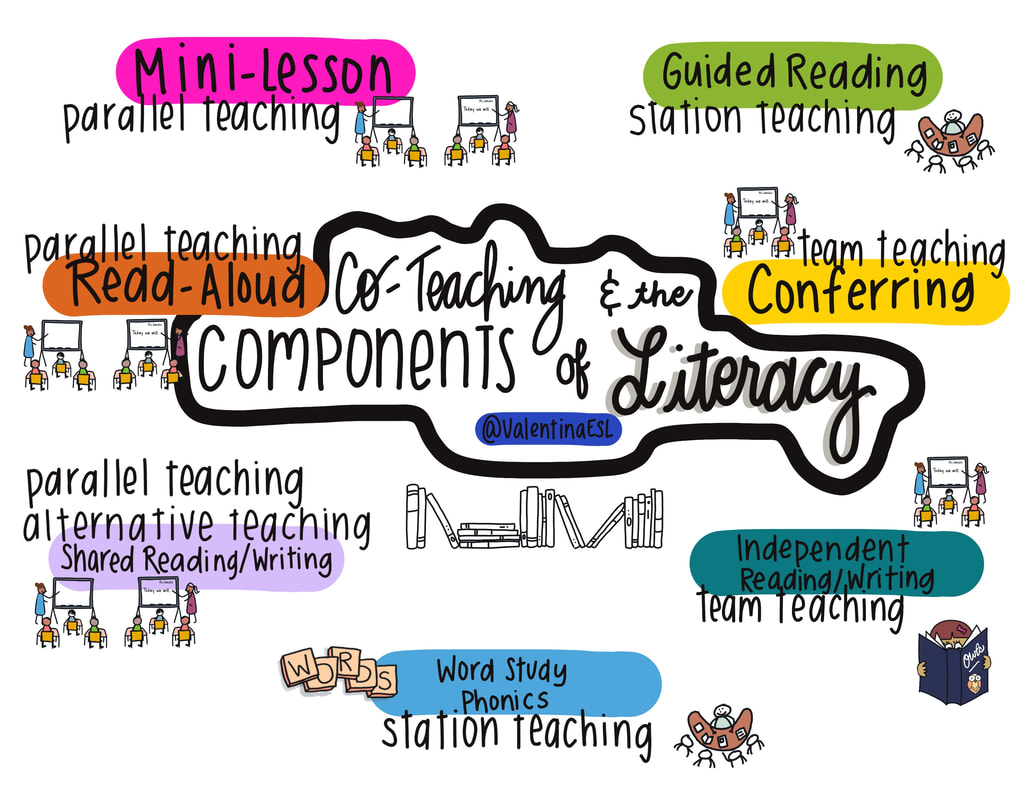
As a co-teacher, you might wonder how co-teaching fits in with the components of literacy. Or you might be a main stream (general education) teacher that has a co-teacher and you wonder how to best utilize two teachers in the room during reading and writing instruction. Many ESL teachers co-teach in classrooms during reading and writing blocks. It's important to know which co-teaching approaches fit best with each component of literacy instruction.
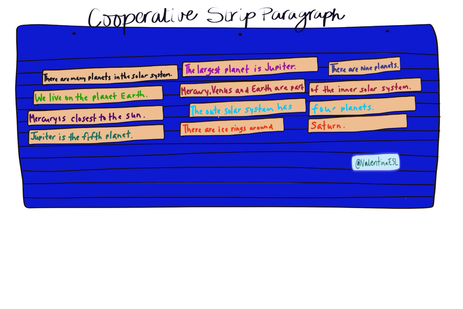
GLAD Strategy: Cooperative Strip Paragraph
What is the cooperative strip paragraph? The Cooperative Strip Paragraph is by far one of my favorite GLAD (Guided Language Acquisition Design) strategies because it promotes cooperative learning, reading and writing in all content areas. BAM! I first learned about it several years ago when I went through GLAD training. I used to be a certified GLAD trainer for my district (but we let our certification expire). The great thing is that even if your certification expires, the knowledge you've gained never does! Anyhow, I instantly fell in love with Cooperative Strip Paragraphs after using them with my own students. What I love most about CSP is that it allows my students to process their learning while they write in cooperative groups, practice reading at their own readability level, and go through the steps of revising and editing in an authentic way using a shared piece of work. And the fact that CSP can be used in any content area K-12 is an additional BONUS!
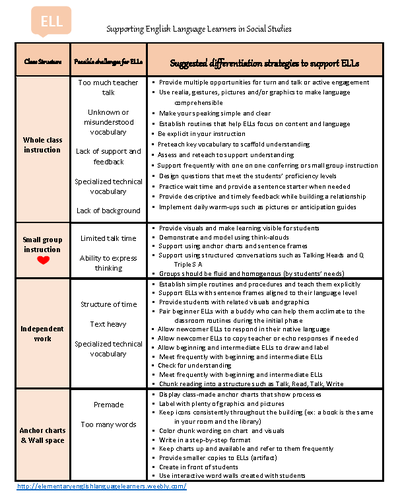
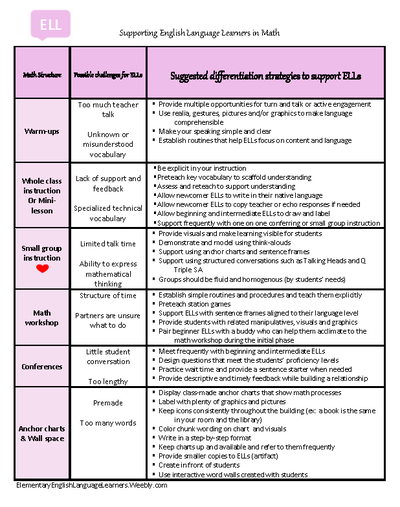
These supporting documents have been in high demand and are in various blog posts on this blog. So I decided to put them all in one post for easy access. This is a one stop shop where you can find the supporting documents to shelter instruction in the content areas. Please feel free to share them with your teacher colleagues as they are meant to help all educators and students. These supports are not just for English Language Learners. ALL learners who need extra help will benefit!
1. Model
Each kid benefits from seeing how to write before they DO the writing. BUT for English Learners this is even more important because language structures may vary from their native language. For example, if I want my students to write about themselves describing their age, I might show them that in English we write: " I am nine years old." This is different from other languages like my native language where a person might say, "I have nine years." Modeling what we expect from students gives them a clear goal for their writing. 2. Be Explicit |
Categories
All
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||






 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
