|
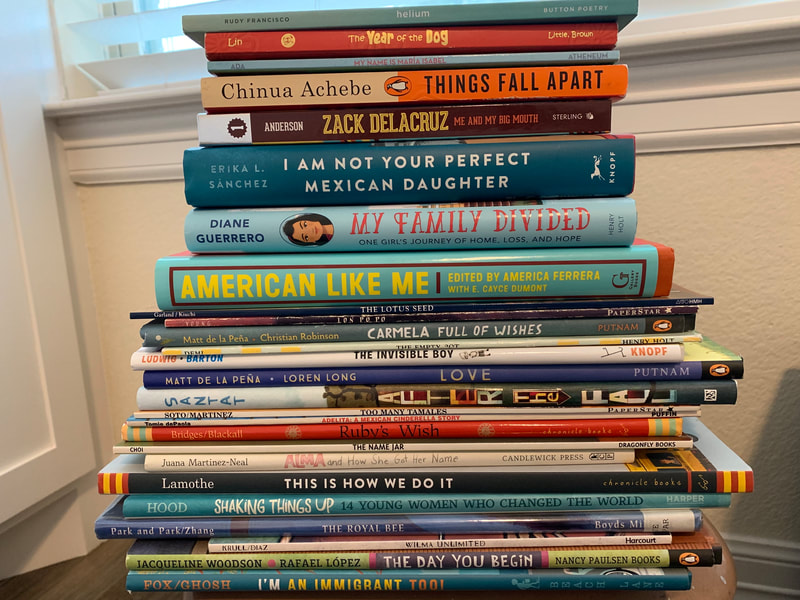
This article was first published on 6/8/2018 and updated on 8/21/2021. When I first saw the graphics below that showed the diversity represented in children's books, I was stunned and appalled. You can learn more about the article here. The statistics were alarming. They reported that the majority of main characters depicted in children's books are either White or Animals/Objects. Seeing these graphics and reading about the study led me to take an audit of my own books and resources. I started by sorting out my books. I made stacks. And honestly, I was shocked and saddened that my bookshelf truly was not as diverse as I imagined. It certainly did not parallel the demographics on my campus either. This prompted action. Students benefit from seeing themselves and others in the books they read. Why? For one, because seeing ourselves outside of ourselves makes us feel visible. In this video, Rene Watson, an author and educator, shares how important it is for students to read about about characters that are like them and share similar experiences. Rudine Sims-Bishop calls these books mirrors. On the other hand, readers also need to read about a wide variety of people and experiences. Sims-Bishop calls these windows. Reading about other's lives helps us to find connections and build community. Dr. Brene Brown says, "We are hardwired for connection and without it there is suffering." We also gain much knowledge and learn empathy from seeing others in the books we read. So why aren't our shelves filled with books that have diverse characters? If you've ever questioned why your students aren't interested in the books on your shelves, you might stop to think about the types of books that are there. Do they represent your students? Can the kids connect with them? I also learned about a non-profit organization called We Need Diverse Books. Check it out. They share a lot of information including lists of diverse books. In my quest for making my shelf more diverse, I have found some great books. I'll keep adding to this and if you have suggestions, please comment and include a picture if you can. If you like what you read and would like to read more like this, you may enjoy the book Reading & Writing with English Learners: A Framework for K-5 by Valentina Gonzalez and Dr. Melinda Miller.
For several years I taught on a campus that had an ESL program. We had students from around the globe. Families literally sought out our school before signing a lease or purchasing a home because they wanted to be sure their kids would be zoned to our campus. Our program was well known for the success we had with multilingual children.
The Stepping Stones that Led me hereOver the past few years, teachers often ask me how I went from a classroom teacher to an educational consultant and author. They are curious and many would like to follow the path. It’s no secret. I’m happy to share it with you. If you’re curious or perhaps have a similar desire, read on.
About this time of year dozens of articles come out about how to support English learners during the summer so their English language development doesn’t regress. Many with good intentions recommend families push English as a main or pervasive language. Historically, it was thought that students that were learning English needed to shed their heritage language to “make room” for English. Now we know that theory is not true and that a heritage language supports the development of additional languages. So what should we advise caregivers to do at home over the summer to keep their children learning and prepared for the next school year?
On May 11, I had the honor to sit in a virtual room with THE Regie Routman about teaching readers NOT teaching reading. Yes, we carefully thought that out because we both believe the center of instruction should be around children always. I'm delighted to share this conversation with you.
Teaching multilingual children is a gift. It’s truly a joy. In my own classroom, I learned so much from my students, especially those that spoke more than one language.
Over the years, one thing I learned from experience as well as through professional learning is that each student deserves to be seen and served individually. No one size fits all approach works. While differentiation may seem daunting, it’s actually not that scary. Dr. Stephen Fleenor describes differentiation as “not creating individualized lessons...it is creating environments in which students at all different levels, all different proficiencies...can each thrive and each grow one level up in that lesson”. Dr. Fleenor offers two wise suggestions for creating of environments that offer differentiation: Last year, I wrote about what I was currently listening to, reading, writing, and viewing. I thought it was a good time to share again. And I’d love to learn about yours!
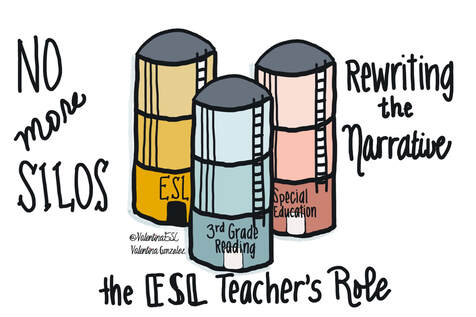
EL teachers work alongside many stakeholders. They work with students of course. But they also work with general education teachers, instructional coaches, special education teachers, administrators, and more. However, one lesser known, yet powerful partnership is the one between the EL teacher and the library media specialist.
What do EL teachers and library media specialists have in common? These stories from the field bring a reality to the question. This article was originally shared on the Seidlitz Blog on April 29, 2020.
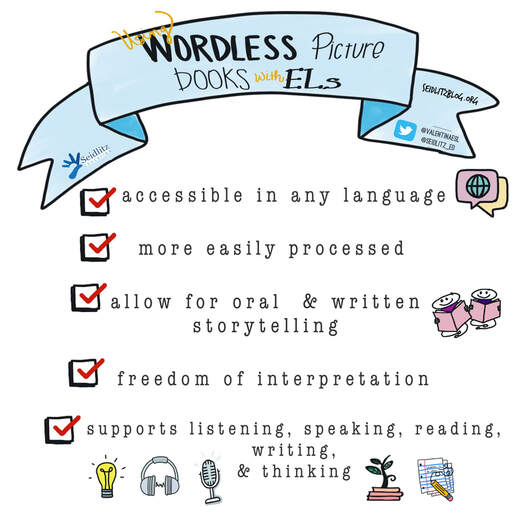
Imagine you are a second grade student born in America, and you only speak English. You’ve attended English schools until now. But your father’s job has relocated your family to France, and now you are in a classroom filled with students and a teacher who only speak French (a language you have never spoken). The science teacher hands you a book and signals for you to read it. You open the book and find that it is filled with pictures…no words. First a group of horses. A mare feeding a foal. A colt running wild. Then a group of pigs, chickens, cows, etc. Instantly, you begin to think about the information you know about animals. What they are called, where they live, what they eat, etc. Though you aren’t able to communicate this information in French yet, you are able to follow along with the class and think in English using the schema and background knowledge you have about animals. Why Use Wordless Picture Books? If you are new to teaching English learners or new to your role as an EL/ESL/ELD/ELL teacher, these are articles you may find useful.
A lot of the work I do centers around literacy and ELs. The goal of this post is to help you quickly & easily find what you're looking for as a reading teacher of ELs.
Leading is more about what you choose to do rather than the title you have. Like most of you, I've witnessed many campus teachers who were amazing examples of trailblazers who were the epitome of excellence and who all the other teachers looked up to, went to advice for, and wanted to be like. These were the educators who inspired others and lit flames!
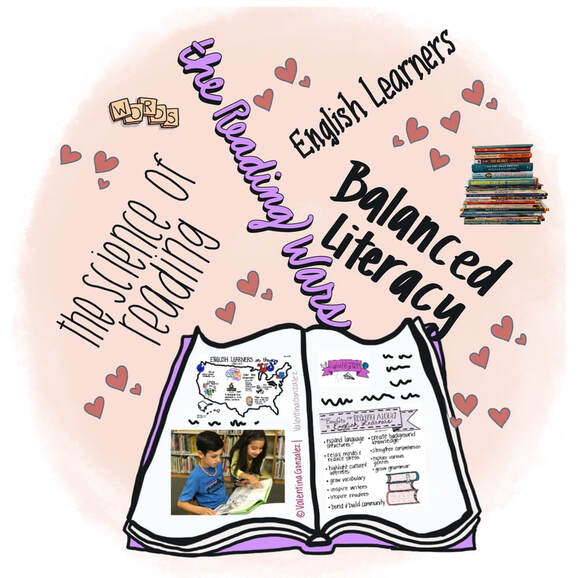
On the other hand I'v also seen professionals with elaborate titles who did the bare minimum and often created tension or were like a firework that was a dud...you hoped it would ignite into a beautiful burst of colors, but instead it fizzled into a messy, smelly smoke bomb. Such a disappointment. If you teach reading you have probably heard of the “Reading Wars”. And if you haven’t, then perhaps you don’t even need to read any further. For those that have, you might feel confused. I, for example, question why we have to “be at war” with colleagues or pick a side. I don’t want to be at war or pick a side. But the tension on Twitter and Facebook is real.
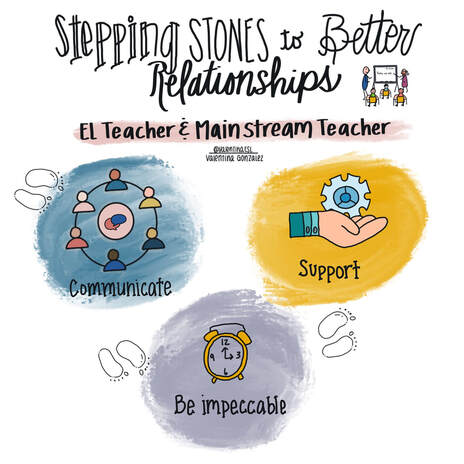
In essence the debate is about how best to teach reading to students. But many educators wonder if we can believe in both balanced literacy and the science of reading? When I left the comfort of my own classroom to become an ESL teacher, I didn’t know that I would have to become intentional about building relationships with the mainstream classroom teachers I worked with. But I learned quickly.
Healthy, productive relationships between mainstream teachers and ESL teachers don’t happen on their own magically. Like most relationships, thought, planning, and careful execution takes place for a truly happy relationship to develop. Over the years, here’s what I learned as an ESL teacher about creating relationships with mainstream teachers. I am beyond excited about the publishing of my first book! This book is truly a labor of love and comes from my heart. And I'm honored to have co-authored it with Dr. Melinda Miller. She and I compliment one another beautifully. As I think back on my why, why did I write this book, I'm taken back to my own years in elementary school as an English learner. Even though school came very naturally to me, reading didn't. Don't get me wrong. I could decode like it was anyone's business. But I didn't have a desire or stamina for reading. One year, I had an awesome reading teacher who let us read whatever we wanted during independent reading block. AND we routinely had independent reading time. The problem was that I wasn't connecting with books. Instead, I found myself hiding behind the pages and peering over to wonder what my classmates were doing. I was a good student. Straight As. A teacher's pet for sure! I wanted to please so I mimicked everyone else. But deep inside I just wanted to figure out why everyone else was actually reading. The funny thing is that my experiences as an EL didn't magically make me understand how to teach ELs reading and writing. Sure, I could empathize and I had my own background knowledge to lean on, but as a teacher, I had to seek out a ton of professional learning, books, and PD on the topic before I felt like I was really making progress. I hope you find what you're looking for in this book. I hope you see yourself as a teacher, leader, and role model. I hope it stirs up something inside of you and creates a new passion and desire for serving ELs. 10 Reasons Why YOU Should Read Reading & Writing With English Learners; 1. You want to help English learners become stronger readers. 2. You want to help ELs love writing. 3. You want to be a better reading teacher for your students. 4. You want to strengthen your skills as a writing teacher. 5. You want to increase ELs' language and literacy. 6. You want to learn more about a balanced literacy approach. 7. You want to find out how to accommodate reading and writing instruction to support ELs. 8. You want ELs to succeed and feel they belong in grade level ELA classrooms. 9. You want to provide ELs with the best reading and writing support they can have. 10. You want to be equipped to serve ELs in reading and writing workshop. This article was originally posted on 2-25-2017 and has been updated on 9-17-2020 to include information relevant to distance learning.
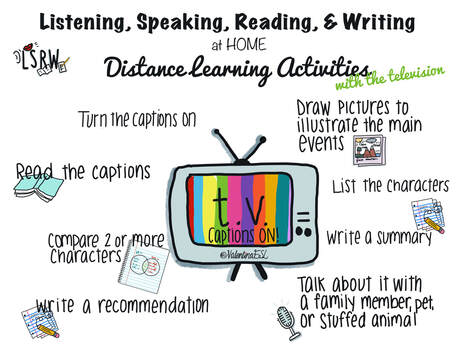
“A picture is worth a thousand words" or so we’ve heard. The question is, how do we encourage students to get those words out, especially if we are teaching and learning in remote or hybrid settings? Some of you may be familiar with the Picture Word Inductive Model (PWIM) which was first introduced by Emily Calhoun (1999). This instructional method has been successful in traditional classrooms for decades, but can we implement it in virtual settings too? Read on to find out what PWIM is and how you can implement it to develop language. If we want to ensure that English learners don't continue to fall behind academically, integrating language with content is the key! This is where listening, speaking, reading, writing, (and viewing) come into play. So I ask you, how are you practicing what you preach and modeling these behaviors for staff, students, and families? I'll share mine and then I'd love to hear yours!
Listening... I started teaching in the winter of 1997. Hired in a wonderful suburban district outside of Houston, Texas. The campus experienced a little growth and needed a teacher mid year, so I was the lucky one hired in December just as I received my college diploma and teaching certification.
My college pre-service classes taught me little about what the classroom experience would truly be like. And with wide-eyes I walked into my first classroom and found myself teaching third graders who had a myriad of needs I was ill prepared for. Some students needed special education support, others dyslexia, and some were learning English. I quickly found that the big white binder of curriculum didn’t hold the answers I needed to give these kids the support THEY needed. Art teacher, Libby Beaty, teaches in Seoul, South Korea at Seoul Foreign Middle School. I came across her Twitter handle in April and was instantly hooked. But I didn’t know how much I would actually love her until after I asked her to answer a few questions for me. When I read her responses, my heart filled with joy and I couldn’t wipe the smile off my face. It was Teacher Appreciation Week and this is yet another example of a teacher we must celebrate!
Here's the art project that Libby shared on Twitter and that she had her students do. It went pretty much viral. When I saw it, I reached out to Libby on Instagram and asked if I could “interview” her about her work. I asked her a series of questions. Here’s how it went. I'm hearing from colleagues, family members, close friends, and educators around the globe that they are worried about students not getting enough instructional time right now while schools are closed due to the Corona virus. Parents are stressed. Teachers are overworked. Kids are confused. And we're all just trying to figure this out while it's happening (very quickly)!
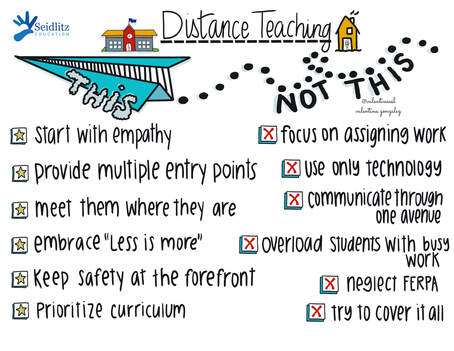
The biggest concern from teachers is about the kids they aren't hearing from on online platforms or through other means of communication. What are they doing? Are they learning? What's going on? And how can I help? Guess what...students are learning a lot at home. We might just have to help families refine daily practices a little. So here's what I suggest. If you'd like to watch the free, brief webinars that Tan Huynh and I did on Reading and Writing with ELs during Distance Learning, they are available on this website along with the presentation slides. Stay well friends. Pivoting instruction to meet the needs of students and families has been a challenge for teachers across the world since the COVID-19 pandemic. But through collaboration and continued support, we are working together to serve students. Thank you all for everything you are doing to ensure that ELs are receiving the support they need.
This article originally posted on Middle Web on 1/6/2019. This is an updated version that includes how to promote academic language during distance learning.
“My kids seem to speak English well, but when it comes to academic tasks, they struggle.” We often wonder why English learners have a difficult time with standardized tests and essays in content areas but are able to communicate with peers and get along fairly well on a day to day basis. The reason behind it may be that academic language is different from everyday language. Academic language takes from 5-7 years to acquire while social or conversational language (often known as BICS, basic interpersonal communicative skills coined by Jim Cummins) only takes 2-3 years. What we know is that students need to make greater gains in academic language in order to become successful in school and post secondary. Academic language is the language of the content area of instruction. It is the textbook talk and vocabulary and syntax used in lectures and class presentation. It is not just single words and includes phrases and sentences as well. It is critical that English learners are offered many opportunities on a daily basis to practice using academic language. Why? We have to consider that some English learners go home to environments where they speak another language in the home. And that is awesome! Bilingualism has great benefits. However, to develop bilingualism, when they are in our classrooms or under our instruction, we have to build as many opportunities as possible for English language development using domain specific vocabulary. We have to put the language in their mouths. Other students (including native English speaking students) may go home to English speaking households, but the level of vocabulary or conversation may not be where we’d hope. This is yet another reason why our instruction (be it face to face or remote) needs to be filled with opportunities for students to use academic language. How can we get students to use academic language? Below you will find 10 ways to get students, especially English learners, practicing academic language in your classroom and beyond. He was born in the U.S. Is he lazy? unmotivated? what's going on?
If you teach middle school or high school you can probably relate. You may have asked yourself this question before, “Why hasn’t this EL met exit criteria?” Are they lazy? Are they not trying? Are they unmotivated? What is going on?
Let’s look at a student profile:
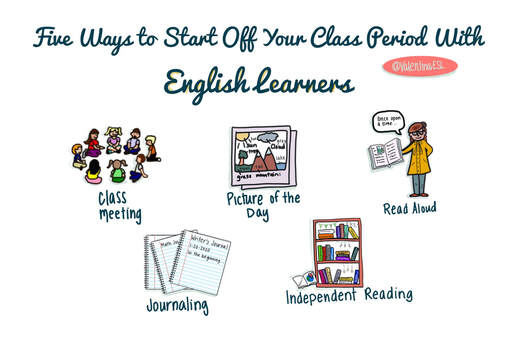
Why haven’t they met criteria to exit ESL? There may be many factors that contribute to students remaining in ESL and not meeting exit criteria. Examining each student’s profile closely could reveal the answer. However here a few common problems that lead to long term EL status: The first thing we do with students can set the tone for our time together. Starting the period off on the right foot is critical to a successful lesson. Read on to discover five ways to start your class period in engaging and welcoming ways whether you are a general education teacher or an ESL teacher that pulls students out.
This question has been asked a time or two (hundred...thousand…). Seriously though. In districts around our nation some ESL teachers are considered part of the intervention team while others are not. Why is this important?
Merriam Webster’s definition of intervention: a : the act of interfering with the outcome or course especially of a condition or process (as to prevent harm or improve functioning) educational intervention To clarify, ... |
Categories
All
|





















































 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
